

|
|
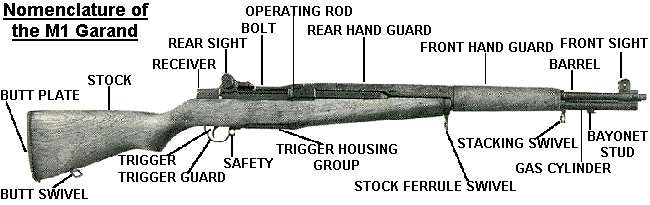
"THE KMI RIFLE"
![]()
| KMI
used the M1 Garand rifle (without firing pins) as our parade ground and
drill team carry rifle. All KMI cadets were required to learned
to field strip their assigned M1 Grand and put it back together in a
timed exercise. Some of us even did it with our eyes
closed! Needless to say, the process could become dangerous when
setting the recoil spring! We all had to disassemble and clean
our assigned Garands each week during the school year. Yes, we
did have to memorize our assigned M1's serial number!!! |
|

M1 GARAND |

M1 GARAND |
  | |
| SOURCE: Wikipedia The M1 Garand (officially the United States Rifle, Caliber .30, M1) was the first semi-automatic rifle to be generally issued to the infantry of any nation. In 1936, it officially replaced the bolt-action Springfield M1903 rifle as the standard service rifle of the United States military (the M1903 retaining a valuable role as a sniper rifle), and was subsequently replaced by the selective-fire M14 in 1957. However, the M1 continued to be used in large numbers until 1963, and to a lesser degree until 1966. The M1 was used heavily by U.S. forces in World War II, the Korean War, and, to a limited extent, the Vietnam War. Most M1 rifles were issued to American Army and Marine troops, though many thousands were also lent or provided as foreign aid to America's allies. The Garand is still used by drill teams and military honor guards. It is also widely sought by the civilian population as a hunting rifle, target rifle, and military collectible. The name "Garand" is pronounced variously as [gəˈrænd] or [ˈgærənd]. According to experts and people who knew Garand, the latter version is preferred.[3][4] |
|
John Garand: The Forgotten History of the Man Who Invented the Iconic M1 Garand Rifle |
|
| Any gun nut – er, “firearms enthusiasts" – worth their salt has heard of the M1 Garand (it rhymes with
“errand,” by the way). This .30-06 semi-automatic rifle is one of the
most iconic American firearms of all time, and was the standard-issue
weapon for American infantry troops during World War II and the Korean
War. Drill teams and honor guards continue to use this in the present
day, such is its role as a symbol of the American military. Fewer, however, know about the life story of the man behind the weapon – John Garand, a Canadian-American engineer and weapons designer. Born one of a whopping 12 children on a Quebec farm, Garand’s father relocated the entire family to Connecticut following the untimely death of the clan’s mother in 1899. All six boys in the family had the official first name St. Jean le Baptiste, however, John Garand was the only one of them who used “Jean” as his first name. The other five used their middle names. The invention bug ran in the family, with several of his brothers sharing his penchant for innovation. Garand learned how to speak English while working in a textile mill sweeping floors. He later worked in a shooting gallery where he developed an interest in firearms, which, when combined with his naturally innovative nature and machining skills picked up in the textile mill, got him a job at a Providence, RI, tool-making company in 1909. In 1916, he relocated to New York City, where he continued working as a toolmaker, and practiced his rifle skills at shooting galleries on Broadway. Garand became a naturalized citizen in 1920. It was in 1917, the same year that the United States entered the First World War, that Garand took his interest in firearms and aptitude at machining and made them into a vocation rather than an avocation. The United States Army was on the lookout for a light machine gun, and the then-more-honestly-named War Department purchased Garand’s design toward that end. Garand himself was given a position with the United States Bureau of Standard. His design was not produced until 1919, the year after the war ended, but Garand was given a government job at the Springfield Armory, which he kept until his retirement in 1953. Garand’s goal might sound unremarkable to us today, but it was a fresh innovation at the time: The U.S. government charged him with creating a gas-actuated, self-loading rifle for the infantry and a carbine capable of ejecting the spent cartridge while also reloading a new round based on a gas-operated system. It took him 15 years to meet the Army’s specifications, but he eventually did it with the M1 Garand. The Garand rifle replaced the bolt-action M1903 Springfield as the standard-issue weapon for infantrymen in the United States military. All told, a whopping four million of these were handed out during the Second World War. No less an authority than General George S. Patton wrote that “In my opinion, the M1 rifle is the greatest battle implement ever devised.” John Garand’s Non-Monetary Rewards Garand never received any royalties for his work on the rifle. A bill was eventually introduced in Congress to award him $100,000 in thanks for his work, but it failed to pass. He died in 1974, in Springfield, MA, where he is interred in Hillcrest Park Cemetery. He did, however, receive non-financial accolades for creating the rifle that would define a generation of American infantrymen. He received the Meritorious Civilian Service Award in 1941, the inaugural Medal for Merit (jointly with Albert Hoyt Taylor) on March 28, 1944, and the Alexander L. Holley Medal from the American Society of Mechanical Engineers. The U.S. Army Ordnance Corps Hall of Fame inducted him the year after his passing in 1974. While the weapon was used in World War II and the Korean War, it saw action in a number of other conflicts around the world, including the Indochina War, the Vietnam War, the Six-Day War, Iran-Iraq War and even the Syrian Civil War. Indeed, there seems to be few conflicts since its invention that the Garand has not been involved in. This is largely due to the weapon’s astonishing durability. The Garand Rifle The M14 was officially adopted in 1957, but it was not until 1965 that the changeover was complete, which was limited to the regular, active-duty Army. The Army Reserve, Army National Guard and the Navy continued to use the weapon well into the 1970s. The U.S. Marine Corps Silent Drill Team, the U.S. Air Force Auxiliary, the United States Air Force Academy Cadet Honor Guard and almost all Reserve Officer Training Corps (ROTC), as well as some Junior Reserve Officer Training Corps (JROTC) still use the weapon when drilling. Imitation is the sincerest form of flattery, and the M1 Garand has no shortage of copies to boast. The Japanese Type 4 is basically a wholesale copy of the weapon, albeit adapted for a caliber more popular in Japan. At the request of NATO, Beretta produced parts of the Garand, including one that was licensed to an Indonesian company. The American M14 is little more than an improved, select-fire version of the M1 Garand, boasting a 20-round magazine chambered for .308. The Ruger Mini-14 is likewise based on the Garand, as is a commercial version of the weapon produced stateside. Certain American citizens who meet requirements set forth by the Civilian Marksmanship Program can own the real deal. Garand’s carbine, sadly, remained a prototype. While not as famous as Thomas Edison or Henry Ford, John Garand is no less important in the history of American innovation. Indeed, his genius might well be responsible for the resounding success of the American war effort. If you value the freedom you hold as an American, take a moment to remember the life of John Garand, a man of humble beginnings whose innovation holds a resoundingly far reach in American and world history. Written by Sam Jacobs AMMO.COM |
|

M1 GARAND |

M1 GARAND |

| Kentucky
Military Institute
www.kmialumni.org Send e-mail to: kmimail@kmialumni.org Copyright © All rights reserved. |
 |